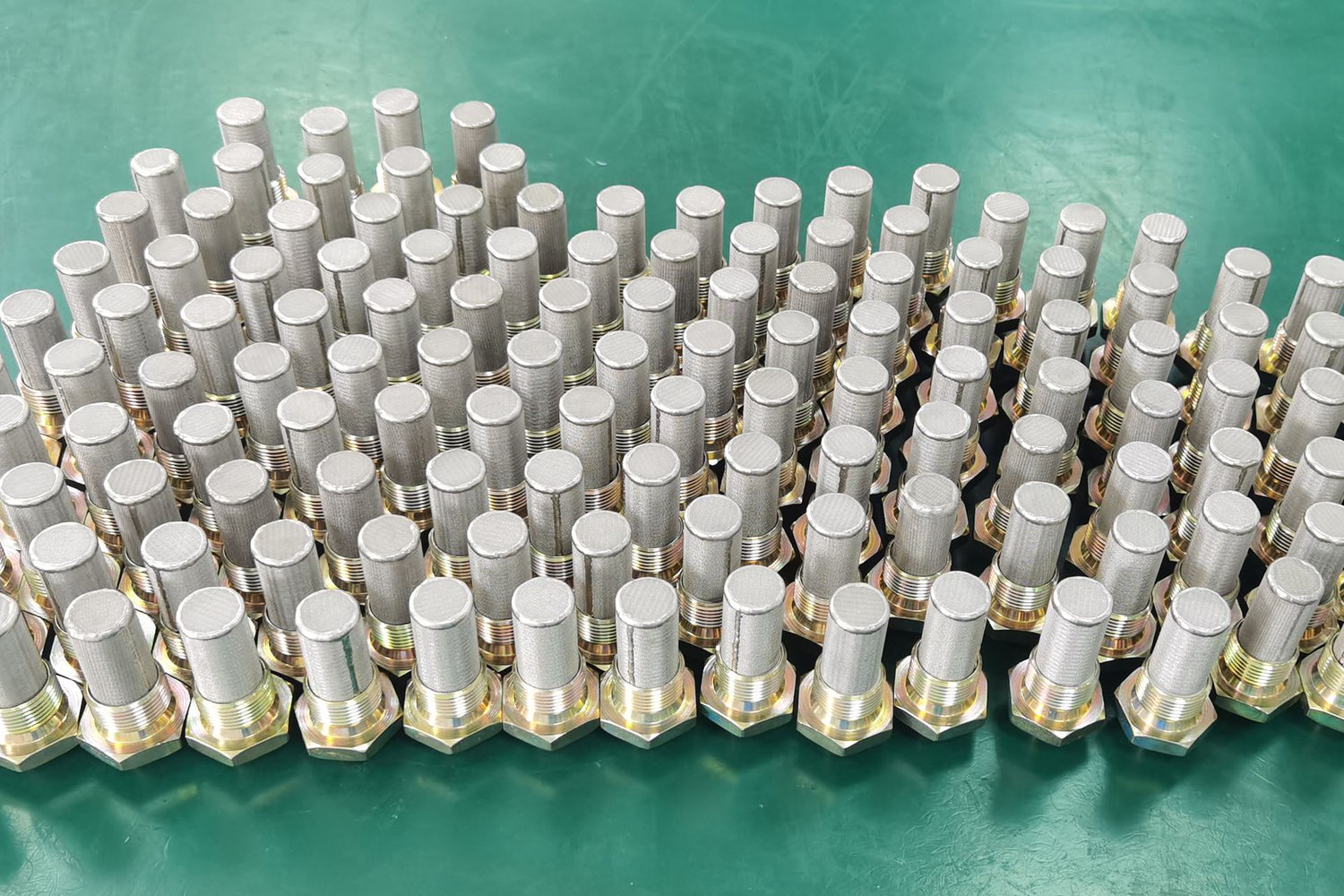
What is a high pressure hydraulic filter?A high pressure hydraulic filter is a crucial component in hydraulic systems that is responsible for removing contaminants from the fluid to ensure smooth operation of the system. It helps prevent damage to sensitive components and extends the lifespan of the equipment.Benefits of Using a High Pressure Hydraulic FilterUsing a high pressure hydraulic filter offers numerous benefits, such as improved system performance, reduced maintenance costs, increased equipment lifespan, and greater efficiency. It also helps prevent system failures and downtime, saving time and resources in the long run.How Does a High Pressure Hydraulic Filter Work?A high pressure hydraulic filter works by trapping contaminants like dirt, debris, and metal particles from the fluid as it passes through the filter media. This helps maintain clean hydraulic fluid, which is essential for the proper functioning of the system and prevents damage to critical components.Types of High Pressure Hydraulic FiltersThere are various types of high pressure hydraulic filters available, including in-line filters, spin-on filters, cartridge filters, and tank-mounted filters. Each type has its own unique features and benefits, so it's important to choose the right filter based on the specific requirements of the hydraulic system.Importance of Regular MaintenanceRegular maintenance of a high pressure hydraulic filter is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the hydraulic system. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer's guidelines for filter replacement intervals and to monitor the condition of the filter regularly to prevent any issues.Factors to Consider When Choosing a High Pressure Hydraulic FilterWhen selecting a high pressure hydraulic filter, it is important to consider factors such as flow rate, pressure rating, micron rating, compatibility with the fluid, and the environment in which the system operates. By choosing the right filter, you can effectively protect your hydraulic system.Common Contaminants Removed by High Pressure Hydraulic FiltersHigh pressure hydraulic filters are designed to remove various contaminants from the fluid, including dirt, dust, metal particles, water, sludge, and other impurities. By effectively capturing these contaminants, the filter helps maintain clean hydraulic fluid and prevents system damage.Signs of a Clogged High Pressure Hydraulic FilterA clogged high pressure hydraulic filter can lead to decreased system performance, increased pressure drop, fluid leaks, and unusual noises. It is important to be aware of these signs and address them promptly by replacing the filter to avoid costly repairs and downtime.Importance of Using Quality FiltersUsing high-quality filters is crucial for the proper functioning of a hydraulic system. Quality filters are designed to withstand high pressures, resist clogging, and effectively remove contaminants from the fluid. Investing in quality filters can help prevent costly repairs and downtime.ConclusionIn conclusion, a high pressure hydraulic filter plays a critical role in maintaining the efficiency, performance, and longevity of hydraulic systems. By using quality filters, regularly maintaining them, and choosing the right type for your system, you can ensure smooth operation and prevent costly downtime and repairs.Quote Inquirycontact us